About the Course
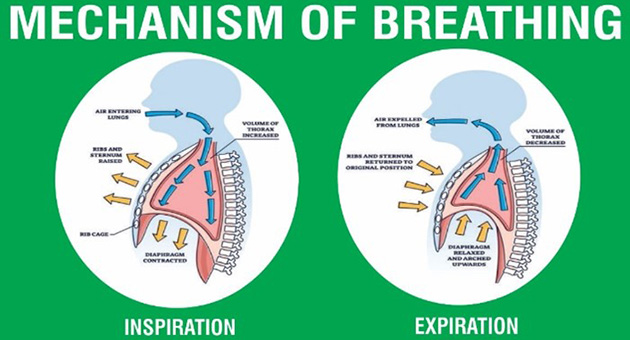
Breathing is a vital process that involves the coordinated action of various muscles and organs to ensure the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, essential for sustaining life. During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, while the intercostal muscles lift the ribs, expanding the chest cavity and reducing internal pressure. This expansion allows air to enter the lungs through the nose or mouth, traveling down the trachea and into the bronchi. Within the lungs, gas exchange occurs as oxygen from the inhaled air diffuses across the alveolar membranes into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli. In contrast, exhalation involves the relaxation of the diaphragm, which moves upward, and the lowering of the ribs by the intercostal muscles. This decreases the chest volume, increasing internal pressure and pushing carbon dioxide-rich air out of the lungs through the airways. Understanding these mechanisms forms the foundation for comprehending respiratory health and its significance in overall well-being.-
Lesson - Mechanism of Breathing
Video
-
Assessment
Assessment
-
Discussion Forum
Discussion Forum
-
Feedback
Feedback
There are no reviews for this course yet.